






































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of pharmacovigilance systems, focusing on srs (suspected adverse reaction) databases such as fda adverse event reporting system (aers) and cdc/fda vaccine adverse events (vaers). It discusses the weaknesses of srs data, reporting odds ratios and incidence rate ratios, and existing methods like bayesian logistic regression and propensity score. The document also touches upon the challenges of extreme sampling variability and simpson's paradox.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 56

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

















































1
2
Bayesian Logistic Regression
Bayesian Logistic Regression
Propensity Score
Propensity Score
4
5
Databases of Spontaneous
Databases of Spontaneous ADRs
ADRs
FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS)
FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS)
Online 1997
Online 1997
replace the SRS
replace the SRS
Over 250,
Over 250, ADRs
ADRs reports annually
reports annually
15,000 drugs - 16,
15,000 drugs - 16, ADRs
ADRs
CDC/FDA Vaccine Adverse Events (VAERS)
CDC/FDA Vaccine Adverse Events (VAERS)
Initiated in 1990Initiated in 1990
12,000 reports per year
12,000 reports per year
50 vaccines and 700 adverse events
50 vaccines and 700 adverse events
Other SRS
Other SRS
WHO - international
WHO - international pharmacovigilance
pharmacovigilance program
program
7
Multi-item Gamma Poisson
Multi-item Gamma Poisson Shrinker
Shrinker (MGPS)
(MGPS)
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network
Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network
WHO Uppsala Monitoring Centre (UMC)WHO Uppsala Monitoring Centre (UMC)
Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR and
Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR and aPRR
aPRR )
)
UK Medicines Control Agency (MCA)
UK Medicines Control Agency (MCA)
Reporting Odds Ratios and Incidence Rate Ratios
Reporting Odds Ratios and Incidence Rate Ratios
Other national spontaneous reporting centers and drug
Other national spontaneous reporting centers and drug
safety research units
safety research units
8
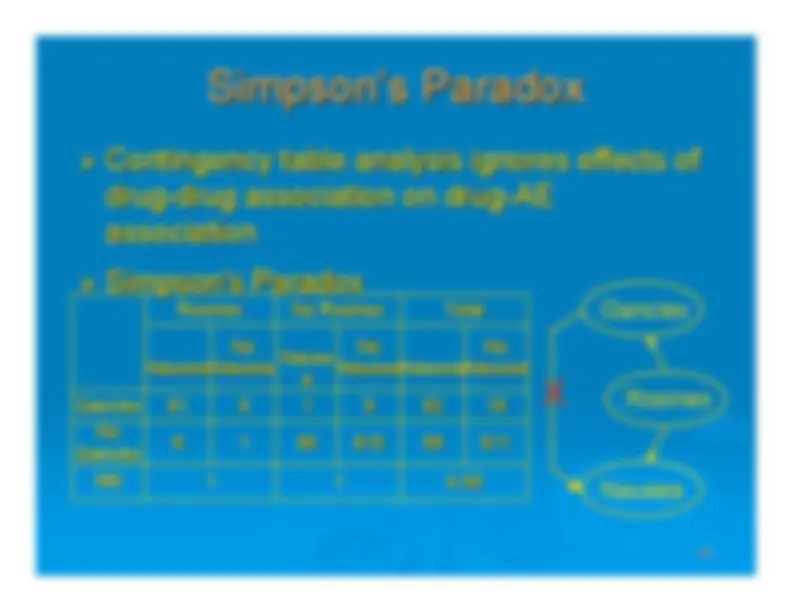
ijij
AE j =
Yes
AE j =
No
Total
Drug i = Yes a =20 b =100 120
Drug i = No c =100 d =980 1080
Total 120 1080 1200
10
10
11
13
13
!
f ( " | data ) =
f ( data | ") f ( ")
f ( data )
!
27
0
"
$
%
&
'
(
0
( 1 ) ()
27
!
c "
a
( 1 # ")
b
!
" #
a + 0
( 1 $ #)
b + 27
16
16
17
Denote by θ
i
Assume θ
i
i
!
19
If the Drug and the AE were independent, what would
If the Drug and the AE were independent, what would
you expect
you expect a
a to be?
to be?
Overall (
Overall ( a
a
c
c )/(
a
a
b
b
c
c
d
d )=120/1200=10% have the AE
)=120/1200=10% have the AE
So, 10% of the
So, 10% of the “
Drug
Drug ”
reports should have the AE
reports should have the AE
That is (That is ( aa ++ bb )(()(( aa ++ cc )/()/( aa ++ bb ++ cc ++ dd ))=12010%))=12010%=12==12= EE
ijij
Note
Note N
ij
ij
ij
ij
=a/
=a/ (
a
a
b
b )*((
a
a
c
c )/(
a
a
b
b
c
c
d
d ))=RR
= Pr(AE|Drug)/Pr(AE)
= Pr(AE|Drug)/Pr(AE)
d=
d= c=
c=
Not
Not
Drug
Drug
ii
b=
b= a=
a= DrugDrug
ii
Not
Not AE
AE
j
j
AE
AE
j
j
N
N
ijij
20
ijij
ijij
ijij
SimpleSimple
Easy to interpret
Easy to interpret
Extreme sampling variability when baseline and
Extreme sampling variability when baseline and
observed frequencies are small
observed frequencies are small
(
( N
N =1,
=1, E
E =0.01 v.s.
=0.01 v.s. N
N =100,
=100, E
E =1)
=1)
GPS provides a shrinkage estimate of RR that
GPS provides a shrinkage estimate of RR that
addresses this concern.
addresses this concern.
ij
ij
i
j
N..
N.. N.
N.
j
j
Not
Not
Drug
Drug
i
i
N N
ii
NN ..
ijij
Drug
Drug
i
i
Not
Not AE
AE
j
j
AE
AE
j
j