Download lithography techinique described properly and more Lecture notes Very large scale integration (VLSI) in PDF only on Docsity!
Photolithography
Source: Dr. R. B. Darling (UW)
lecture notes on photolithography
Why Lithography?
Simple layers of thin filmsdo not make a device.
To create a device suchas a transistor, layers ofthin films have to bepatterned, etched andcoated.
Lithography combinesthese processes and cancreate millions of devicesin batch.
A MOSFET Device The MOSFET as patterned on a wafer
Steps Used in Photolithography
Surface cleaning
Barrier layer formation (Oxidation)
Spin coating with photoresist
Soft baking
Mask alignment
Exposure
Development
Hard baking
Post process cleaning
Wafer Cleaning - 1
Typical contaminants that must be removed prior tophotoresist coating:
dust from scribing or cleaving (minimized by laser scribing)
atmospheric dust (minimized by good clean room practice) - abrasive particles (from lapping or CMP) - lint from wipers (minimized by using lint-free wipers) - photoresist residue from previous photolithography (minimizedby performing oxygen plasma ashing) - bacteria (minimized by good DI water system) - films from other sources: - solvent residue - H 2 O residue - photoresist or developer residue - oil - silicone
Wafer Cleaning - 3
RCA clean: use for new silicon wafers out of thebox
APW: NH
4
OH (1) + H
2
O
2
(3) + H
2
O (15) @ 70°C
for 15 min.
DI H
2
O rinse for 5 min.
10:1 BOE for 1 min.
DI H
2
O rinse for 5 min.
HPW: HCl (1) + H
2
O
2
(3) + H
2
O (15) @ 70°C for 15
min.
DI H
2
O rinse for 5 min.
Spin & rinse dry
Wafer Priming
Adhesion promoters are used to assist resist coating.
Resist adhesion factors:
moisture content on surface
wetting characteristics of resist - type of primer - delay in exposure and prebake - resist chemistry - surface smoothness - stress from coating process - surface contamination
Ideally want no H
2
O on wafer surface
Wafers are given a “singe” step prior to priming and coating
15 minutes in 80-90°C convection oven
Photoresist Spin Coating
Wafer is held on a spinner chuck by vacuum and resist iscoated to uniform thickness by spin coating.
Typically 3000 - 6000 rpm for 15-30 seconds.
Resist thickness is set by:
primarily resist viscosity
secondarily spinner rotational speed
Resist thickness is given by t = kp
2
/w
1/
, where
k = spinner constant, typically 80-
p = resist solids content in percent - w = spinner rotational speed in rpm/
Most resist thicknesses are 1-
m for commercial Si
processes.
Photoresist Spin Coating
Spinning Artifacts
Striations
~ 30 nm variations in resist thickness due to non-uniform dryingof solvent during spin coating
~ 80-100 mm periodicity, radially out from center of wafer
Edge Bead
residual ridge in resist at edge of wafer
can be up to 20-30 times the nominal thickness of the resist - radius on wafer edge greatly reduces the edge bead height - non-circular wafers greatly increase the edge bead height - edge bead removers are solvents that are spun on after resistcoating and which partially dissolve away the edge bead
Streaks
radial patterns caused by hard particles whose diameter aregreater than the resist thickness
Prebake (Soft Bake) - 1
Used to evaporate the coating solvent and to densify theresist after spin coating.
Typical thermal cycles:
90-100°C for 20 min. in a convection oven
75-85°C for 45 sec. on a hot plate
Commercially, microwave heating or IR lamps are alsoused in production lines.
Hot plating the resist is usually faster, more controllable,and does not trap solvent like convection oven baking.
Prebake (Soft Bake) - 3
Convection ovens:
Solvent at surface of resist is evaporated first, whichcan cause resist to develop impermeable skin,trapping the remaining solvent inside
Heating must go slow to avoid solvent burst effects
Conduction (hot plate):
Need an extremely smooth surface for good thermalcontact and heating uniformity
Temperature rise starts at bottom of wafer and worksupward, more thoroughly evaporating the coatingsolvent
Generally much faster and more suitable forautomation
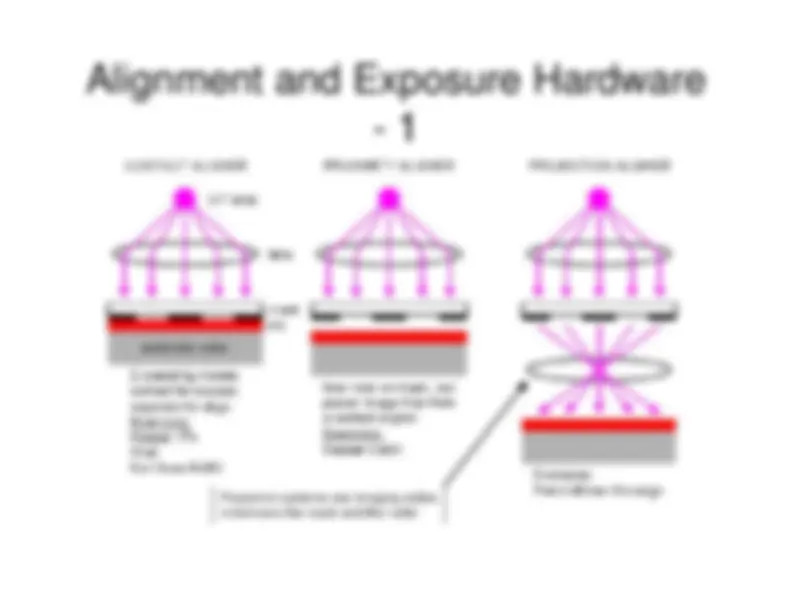
Overview of Align/Expose/Develop Steps
Alignment and Exposure Hardware
2
For simple contact, proximity, and projection systems, the mask isthe same size and scale as the printed wafer pattern. I.e. thereproduction ratio is 1:1. - Projection systems give the ability to change the reproduction ratio.Going to 10:1 reduction allows larger size patterns on the mask,which is more robust to mask defects. - Mask size can get unwieldy for large wafers. - Most wafers contain an array of the same pattern, so only one cell ofthe array is needed on the mask. This system is called Direct Stepon Wafer (DSW). These machines are also called “Steppers” - Example: GCA-4800 (original machine) - Advantage of steppers: only 1 cell of wafer is needed - Disadvantage of steppers: the 1 cell of the wafer on the mask mustbe perfect-- absolutely no defects, since it gets used for all die.
Alignment and Exposure Hardware
3
Higher end research systems go one stepfurther and use Direct Write on Wafer (DWW)exposure systems. - This can be accomplished using:
Excimer lasers for geometries down to 1-2 mm
Electron beams for geometries down to 0.1-0.2 mm
Focused ion beams for geometries down to 0.05-0.1mm
No mask is needed for these technologies. - These are serial processes, and wafer cycletime is proportional to the beam writing time--the smaller the spot, the longer it takes!