Download Module 13 Prenatal Development-1 and more Summaries Development Economics in PDF only on Docsity!
MODULE 13: PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT
LEARNING OUTCOME:
Trace the early beginnings of life and see the principle and pattern of development from conception to full-term fetal development (CLO 3,4). INTRODUCTION All the developmental theories which we lengthily discussed dwelt on the developmental process after birth. None of them was concerned with what development went on before birth. To make the description of human development complete, it may be good to understand the beginnings of the child and the adolescent, the learners (Corpus, 2018). Source: http://mollylindsey.weebly.com/beginnings.html You are familiar with your younger brothers or sisters and you know who they were before they have become what and who they are at present. This is the concern of this Unit and Module – the pre-natal or antenatal development. PREPARATION TASK NO.1:
- Watch the video on Pro-life anti-abortion video at You Tube and High Tech Photographs of Fetal Development.
- Read the “Life Before Birth” below and answer the following questions: a. What are your feelings and reactions about what you read? b. Do you agree that which is developing in the womb is a mere “blob of tissue” or “uterine contents” as abortionists claim?
- Why do you think pregnant mothers are advised not to smoke, not to drink alcoholic drinks, not to take in any medication without doctor’s advice?
- What are the effects of alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine on the developing embryo? PRESENTATION Prenatal development is the process that occurs during the 40 weeks prior to the birth of a child. There are three stages of prenatal development: germinal, embryonic , and fetal. Prenatal development is also organized into three equal trimesters, which do not correspond with the three stages. The first trimester ends with the end of the embryonic stage, the second trimester ends at week 20, and the third trimester ends at birth. Key Points
- There are three stages of prenatal development: germinal, embryonic, and fetal. Prenatal development is also organized into three equal trimesters that do not correspond with the three stages.
- The germinal stage occurs from conception until 2 weeks (implantation), during which the zygote begins to rapidly divide.
- The embryonic stage lasts from implantation (2 weeks) until the 8th week of pregnancy. During this stage, rapid growth occurs and organ systems develop.
- The fetal stage lasts from week 9 until the child’s birth (usually between 38 and 40 weeks). Throughout this stage the brain continues to grow and develop at a rapid pace. Key Terms Embryo : An organism in the earlier stages of development; in humans, usually the cell growth up to the end of the seventh week in utero. Fertilization : The act of impregnating animal or vegetable gametes. Neural tube : A hollow longitudinal dorsal tube formed in the folding and subsequent fusion of the opposite ectodermal folds in the embryo that gives rise to the brain and spinal cord. Zygote : A fertilized egg cell.
Stages of Prenatal Development
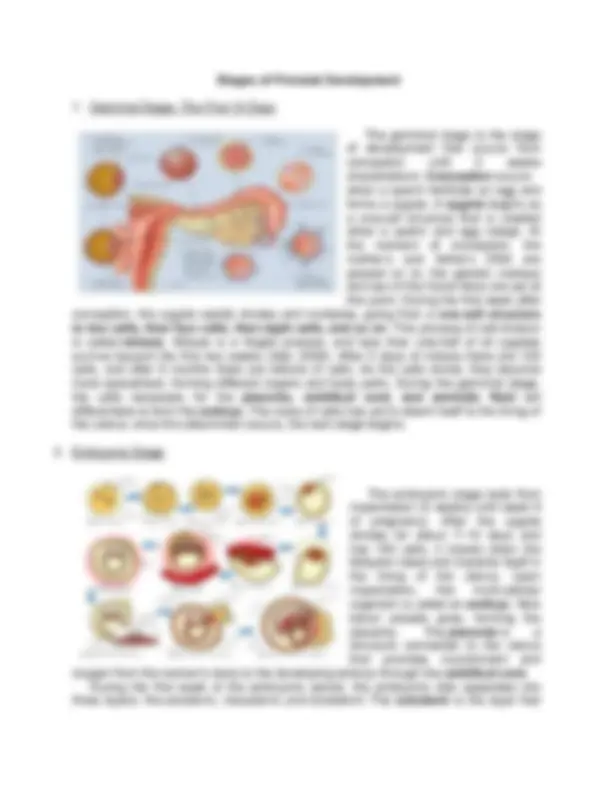
- Germinal Stage: The First 14 Days The germinal stage is the stage of development that occurs from conception until 2 weeks (implantation). Conception occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg and forms a zygote. A zygote begins as a one-cell structure that is created when a sperm and egg merge. At the moment of conception, the mother’s and father’s DNA are passed on to; the genetic makeup and sex of the future fetus are set at this point. During the first week after conception, the zygote rapidly divides and multiplies, going from a one-cell structure to two cells, then four cells, then eight cells, and so on. This process of cell division is called mitosis. Mitosis is a fragile process, and less than one-half of all zygotes survive beyond the first two weeks (Hall, 2004). After 5 days of mitosis there are 100 cells, and after 9 months there are billions of cells. As the cells divide, they become more specialized, forming different organs and body parts. During the germinal stage, the cells necessary for the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic fluid will differentiate to form the embryo. The mass of cells has yet to attach itself to the lining of the uterus; once this attachment occurs, the next stage begins.
- Embryonic Stage The embryonic stage lasts from implantation (2 weeks) until week 8 of pregnancy. After the zygote divides for about 7 – 10 days and has 150 cells, it travels down the fallopian tubes and implants itself in the lining of the uterus. Upon implantation, this multi-cellular organism is called an embryo. Now blood vessels grow, forming the placenta. The placenta is a structure connected to the uterus that provides nourishment and oxygen from the woman’s body to the developing embryo through the umbilical cord. During the first week of the embryonic period, the embryonic disk separates into three layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The ectoderm is the layer that
TERATOLOGY AND HAZARDS TO PARENTAL DEVELOPMENT
Teratology is field that investigates the causes of congenital (birth) defects. Teratogens are any agents from the environment that can cause harm to the developing fetus. It comes from the Greek word “tera” which means “monsters”. Many harmful agents cause damage only if exposure occurs during a sensitive period of prenatal development. About 45% or more pregnancies end in miscarriage, that is, spontaneous abortion. Below are clusters of hazards to pre-natal development:
- Prescription and nonprescription drugs - These include prescription as well as non-prescription drugs. Antibiotic is an example of a prescription drug that can be harmful. Examples of harmful nonprescription drugs are diet pills, aspirin and coffee.
- Psychoactive drugs - These include nicotine, caffeine and illegal drugs such as marijuana, cocaine and heroin. Researchers found that pregnant women who drank more caffeinated coffee were more likely to have preterm deliveries and newborns with lower birthweight compared to their counterparts who did not drink caffeinated coffee. Heavy drinking by pregnant women results to the so called fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) which is a cluster of abnormalities that appears in the children of mothers who drink alcohol heavily during pregnancy. Fetal and neonatal deaths are higher among smoking mothers. On the average, maternal heroin addicts deliver smaller than average size babies with higher incidence of toxemia, premature separation of placenta, retained placenta, hemorrhaging after birth, and breech deliveries (http://www.yale.edu/ynhti/curriculum/units/1980/5/80.05.03.x.html#f).
- Environmental hazards - This include radiation in jobsites and X-rays, environmental pollutants, toxic wastes, and prolonged exposure to heat in saunas and bath tubs.
- Oher maternal factors such as Rubella (German Measles), syphilis, genital herpes, AIDS, nutrition, high anxiety and stress, age, (too early or too late, beyond 30)
- Paternal Factors - Fathers’ exposure to lead, radiation, certain pesticides and petrochemicals may cause abnormalities in sperm that lead to miscarriage or diseases such as childhood cancer. Explore! Know more! _Visit the links below to know more:
- Teratology and Hazards to Prenatal Development by Krisley Tolentino._ https://www.slideshare.net/khrisleytolentino/prenatal-development- 32585156 2. Life Begins at Conception by (Prolife) https://naapc.org/why-life-begins-at-conception/
PRACTICE
TASK NO.2:
I. Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the correct answer.
- The tissue that is connected to the fetus and the placenta that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the fetus is this. A. Ovary C. Ovum B. Fallopian tube D. Umbilical cord
- The name of the developing baby after 8 weeks of pregnancy. A. Zygote C. Embryo B. Fetus D. Conception
- The name of a developing human before 8 weeks is called this. A. Fetus C. Embryo B. Zygote D. Ovum
- In which period are teratogens the most harmful? A. Zygote C. Embryonic B. Fetal D. Germinal
- Which drugs enters the fetuses’ body during the birth process? A. Heroine C. Marijuana B. Cocaine D. Alcohol
- I mplantation is the process of_______. A. An egg and sperm uniting in the uterus B. The placenta attaching to the uterus C. The umbilical cord attaching to the fertilized fetus D. A zygote attaching to the uterus.
- Which common diagnostic test should be avoided if possible during pregnancy? A. Blood test C. Urinalysis B. X-ray D. Ultrasound
- What are the layers of the embryo during the embryonic period? A. Mesosystem and metasystem C. Endoderm and skeletal B. Skin and muscle D. Endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm
- What is a teratogen? A. A measure of prenatal activity B. Any agent which can cause a birth deficit or have negative effects on behavioral or cognitive outcomes C. A physical deformity caused by harmful substances transmitted through the placenta D. A stage of development
PERFORMANCE
TASK NO. 3 :
- Using a PowerPoint presentation, teach the mothers and fathers how pre-natal development takes place and what they should do to ensure normal and healthy development of the embryo. Pass the output through teacher’s email ad for checking.
- Pretend you are “Junior”, 4 months old in the womb. Your Mother is concentrating on doing abortion. Write her a letter convincing her that you are a human being developing contrary to what she and other pro-abortionists are thinking. Describe to her the development that has already take place in 4 months. Reflect what you learned on pre-natal development in this module. Give your letter this title “A letter from Junior” (or you may want to write your name.) ASSIGNMENT TASK NO. 4 : Look at yourself. You are perfectly made. The cells of your lips are at your lips. Your mouth is close to your nose. You can breathe normally. Did it ever occur to you that it could have been otherwise? Any feelings of gratitude? Write down your thoughts here. REFERENCES Books: Corpus, B. (2018). The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles. Lorimar Publishing Inc. Cubao, Quezon City. Metro Manila, Philippines. Online Sources: http://www.yale.edu/ynhti/curriculum/units/1980/5/80.05.03.x.html#f https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundlesspsychology/chapter/prenatal-development/ http://www.mccl.org/Document.Doc?Id=