









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This document offers a concise yet informative overview of neuroimaging techniques used in neuropsychology. it details cat, pet, mri, and fmri scans, outlining their principles, advantages, limitations, and applications in diagnosing neurological conditions and advancing research. The clear explanations and comparative analysis make it a valuable resource for students and researchers.
Typology: Slides
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









Ananya Gupta
What is Neuroimaging?
Neuroimaging, also known as, brain scanning, is a technique to
visualize and study the living brain, providing insights into structure,
function and neurochemistry.
These techniques are used for diagnosis, monitoring treatment, and
advancing research in fields like neuroscience, psychology and
psychiatry.
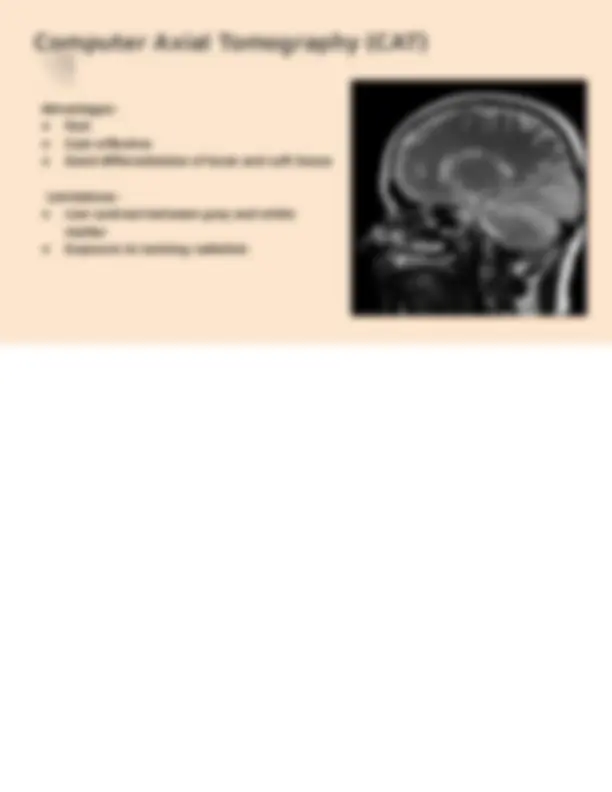
Computer Axial Tomography (CAT)
● CAT, also known as, CT scan uses X-rays and computers to create cross-sectional images of the body/brain.
● The scan rotates around the head, taking x-ray images from different angles which a computer processes into 2D slice images.
● Uses: Detecting tumors, strokes, bleeding, clots, etc. Overall structural imaging.
Computer Axial Tomography (CAT)
Advantages: ● Fast ● Cost-effective ● Good differentiation of bone and soft tissue
Limitations: ● Low contrast between grey and white matter ● Exposure to ionizing radiation
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Some techniques based on MRI-
● MRI Spectroscopy- estimates the concentration of specific chemicals and neurotransmitters in the brain.
● Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)- measures the diffusion of water in tissue and measures the integrity of white matter fiber tracts.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Advantages ● Excellent soft tissue differentiation ● No ionizing radiation exposure ● Imaging in multiple planes
Limitations ● Expensive equipment and scans ● Incompatible with metal implants ● Motion artifacts ● Loud noise
Uses ● Identifying tumors, lesions, abnormalities ● Assessing neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Dementia, etc,. ● Guiding biopsies, therapies, interventions
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Advantages ● Visualizes biochemical/physiological functioning ● Quantifies processes like metabolism, blood flow, neurotransmitters ● Extremely high sensitivity to radiotracers
Limitations ● Requires expensive on-site cyclotron ● Poor spatial resolution ● Radiation exposure from tracers ● Limited clinical accessibility due to high cost Uses ● Identifies areas of altered neurological function ● Aids cancer detection ● Blood flow/metabolism imaging ● Clinical diagnosis with specialized tracers ● Mapping receptors, enzymes, peptides etc.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
● In this technique, changes in the oxygen levels in the blood is tracked to determine brain’s functioning.
● Most active brain regions can be identified by tracking the blood flow.
● The areas of the brain that are working hardest appear brighter on an fMRI scan.
Some comparisons for better understanding
Some comparisons for better understanding