






















































Estude fácil! Tem muito documento disponível na Docsity

Ganhe pontos ajudando outros esrudantes ou compre um plano Premium


Prepare-se para as provas
Estude fácil! Tem muito documento disponível na Docsity
Prepare-se para as provas com trabalhos de outros alunos como você, aqui na Docsity
Os melhores documentos à venda: Trabalhos de alunos formados
Prepare-se com as videoaulas e exercícios resolvidos criados a partir da grade da sua Universidade
Responda perguntas de provas passadas e avalie sua preparação.

Ganhe pontos para baixar
Ganhe pontos ajudando outros esrudantes ou compre um plano Premium
Comunidade
Peça ajuda à comunidade e tire suas dúvidas relacionadas ao estudo
Descubra as melhores universidades em seu país de acordo com os usuários da Docsity
Guias grátis
Baixe gratuitamente nossos guias de estudo, métodos para diminuir a ansiedade, dicas de TCC preparadas pelos professores da Docsity
Solução capitulo 5 Introdução a Circuitos Dorf
Tipologia: Exercícios
1 / 61

Esta página não é visível na pré-visualização
Não perca as partes importantes!






















































Section 5-2: Source Transformations
(a)
= 2
= 0.5 V
t
t
R
v
∴ Ω
−
(b) 9 4 2 ( 0.5) 0
9 ( 0.5) 1.58 A 4 2
i i
i
v = 9 + 4 i = 9 + 4( 1.58)− =2.67 V
(c) (^) ia = i = −1.58 A
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
Finally, apply KVL:
− + i a + ia − = ∴ ia =
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
Finally, apply KVL to loop
− 6 + i (9 + 19) − 36 − v o= 0
i = 5 / 2 ⇒ v o= − 42 + 28 (5 / 2) =28 V
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
a a a
a
i i i
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
− 12 − 6 ia + 24 − 3 ia − 3 = 0 ⇒ ia =1 A
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
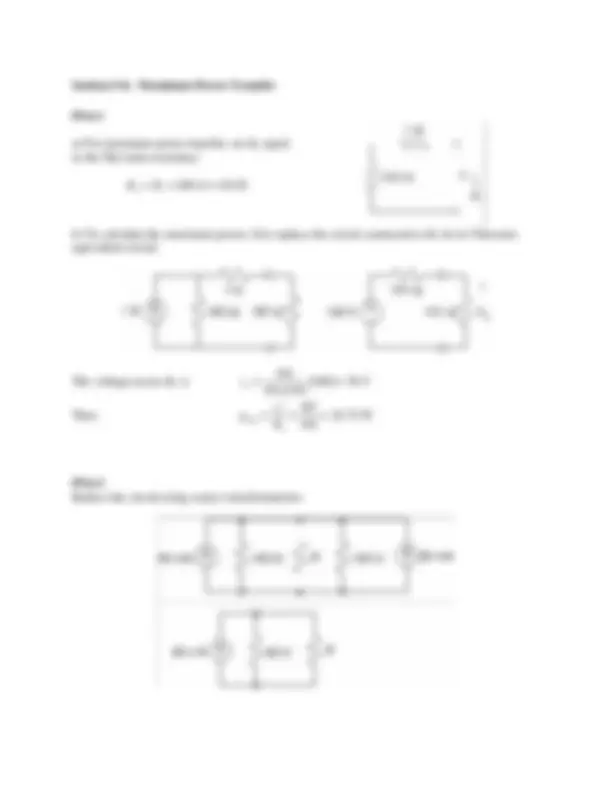
A source transformation on the right side of the circuit, followed by replacing series resistors
with an equivalent resistor:
Source transformations on both the right side and the left side of the circuit:
Label the node voltages.
The 8-V source is connected
between nodes 1 and 3.
Consequently,
v 1 (^) − v 3 = 8
Apply KCL to the supernode corresponding to the 8-V source to get
1 2 3 1 2 3
v v v v v v
Apply KCL at node 2 to get
1 2 2 2 3 =0.04 1 0.19 2 0.1 3 0 25 20 10
v v v v v v v v
Solving, for example using MATLAB
1 1
2 2
3 3
v v
v v
v v
The power supplied by the 8-V source is
4.7873 (^) ( 0.6831) (^) 4.7873 24 8 4.316 W 25 8
Apply KCL at node 4 of the original circuit to get
3 4 4 3 (^ ) 4
v v v v v
The power supplied by the 0.5 A source is
0.5 4.71 ( ) =2.355 W
(checked: LNAP 5/31/04)
Replace series and parallel resistors by an
equivalent resistor.
18 & (^) ( 12 + (^24) ) = 12 Ω
Do a source transformation, then replace
series voltage sources by an equivalent
voltage source.
Do two more source transformations
Now current division gives
8 2 3 8 8
i R R
Then Ohm’s Law gives
24
8
v Ri R
( )
( )
a 2 A 8 4
(b) 12 V 8 8
(c) 1 16 8
(d) 16 16 8
i v R R R R R = =
(checked: LNAP 6/9/04)
Section 5-3 Superposition
Consider 6 A source only (open 9 A source)
Use current division:
1 1
v v
Consider 9 A source only (open 6 A source) Use current division:
2 2
v v
∴ v = v 1 (^) + v 2 = 40 + 40 =80 V
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
Consider 12 V source only (open both current sources)
KVL:
1 1 1
1
1/ 3 mA
i i i
i
Consider 3 mA source only (short 12 V and open 9
mA sources) Current Division:
2
3 mA 16 20 3
i
Consider 9 mA source only (short 12 V and open 3
mA sources)
( )
3
2.5 10 0.5 mA 6 || 6 12 3 12
i
Finally, i = i 1 (^) + i 2 (^) + i 3 = 2 + 2 − 0.5 = 3.5 mA
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
Consider 10 V source only (open 30 mA source and
short the 8 V source)
Let v 1 be the part of v a due to the
10 V voltage source.
( )
( )
( )
1
v =
Consider 8 V source only (open 30 mA source and
short the 10 V source)
Let v 2 be the part of v a due to the
8 V voltage source.
( )
( )
( )
1
v =
Consider 30 mA source only (short both the 10 V
source and the 8 V source) Let v 2 be the part of v a due to the
30 mA current source.
v =
Finally, (^1 2 )
v a = v + v + v = + + =
(checked using LNAP 8/15/02)
Consider 8 V source only (open the 2 A source) Let i 1 be the part of i x due to the 8 V
voltage source.
Apply KVL to the supermesh:
(^6) ( i 1 (^) ) + (^3) ( i 1 (^) ) + (^3) ( i 1 (^) )− 8 = 0
1
i = =
Consider 2 A source only (short the 8 V source) Let i 2 be the part of i x due to the 2 A
current source.
Apply KVL to the supermesh:
(^6) ( i 2 (^) ) + (^3) ( i (^) 2 + (^2) )+ 3 i 2 = 0
2
i
Finally, (^1 )
i (^) x = i + i = − =
Using superposition
s 2 x a 1 2 1 2
v R i i R R R R
. Then
2 o s 1 2 1 2
v v R R R R
i a
When R 1 (^) = 6 Ω, R (^) 2 = 12 Ω and R 3 = 6 Ω
( ) o s
v v A A
i a
Comparing this equation to v (^) o = 2 v s+ 9 , we requires
Then 2 v (^) s + 9 = v (^) o = 2 v s+ 6 i aso we require
9 = 6 i (^) a ⇒ i a=1.5 A
(checked: LNAP 6/22/04)
o1 1 1
v = v = v ⇒
a =
o2 1 2
v = − v = − v ⇒ = −
b
v o3 (^) = (^) ( 8 ||10 || 40 (^) ) i (^) 3 = 4 i 3 ⇒ c = 4
(checked: LNAP 6/22/04)
Using superposition:
v (^) x = 10 i x
and
x x x x
12 cos 2 4 40 10 10
v t v v i
so
x x x
10 12 cos 2 (^12) 2 cos 2 t 40 70
i t i i
Finally,
v (^) x = 10 i x
and
x x x x
v v v i
so
−0.2 = 1.75 i (^) x ⇒ i x= −0.11429 A
Finally,
v (^) o = v (^) o1 + v (^) o2 = 3.429 cos 2 t +2.286 V
(checked: LNAP 6/22/04)
1 2 3
1 2 3 1 1
n R R R (^) n n a R R R n n R R n
1 1 3
2 1 3 1 1
n R R R (^) n (^) n b R R R n n nR R n n
a n b
(b) From (a), we require n =4, i.e. R 2 = 4 R 1 and (^3 1 )
R = R & R = R 1. For example
R 1 (^) = 10 Ω, R (^) 2 = 40 Ω and R 3 = 8 Ω.
(checked: LNAP 6/22/04)
Using superposition
( ) ( )
o 1
v i R R
i 2
Comparing to v (^) o = −0.5 i 1 + 4 , we require
( )
( ) ( )
and
( ) ( )
2 2
i i R
i 2 4 A
(checked LNAP 6/12/04)
Use units of mA, kΩ and V.
4 + (5||20) = 8 kΩ
(a) Using superposition
( )
2 7 2 8 48 16 k 8 8
(b) Using superposition again
a
i
=4 mA
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
1 o 2
3
v i i
v
o 1 2
i v i
v 3
So
a = − 0.05, b = −0.1 and c = −0.
(checked: LNAP 6/19/04)
( )
i m = − = − =
( ) ( )
v m